Variables in COBOL
- A variable is an identifier to hold a particular value or data. It identifies a memory location.
- In COBOL variables are called as Data Names.
- It can be a maximum length of 30 characters.
- Variable must contain only digits(0-9), letters(A-Z), minus sign and Hyphens(-).
- A Variable must not be a reserved word of COBOL.
- A Variable should not contain any space in between, start or at end of the variable name.
Example of Variables
Examples of valid Variables are –
- XYZ
- ABC-123
- A12
- 9ABC
Examples of in-valid Variables are –
- 123_ABC – It does not allow Hyphen
- ACCEPT – This is a reserved word in COBOL
- ABC) – It does not allow Special characters
- MIK+*89
In the diagram which is shown below, we can see how variables are defined in COBOL.
Literals in COBOL
a) Literals are constants in COBOL. And it is directly hard-coded in the program
b) Literals are of 2 types-
Numeric literal
- Numeric literal allows a maximum of 18 numbers. Valid values allowed are
- 0 to 9 (any number)
- One sign only( either + or -) which has to be used in left side only
- One decimal only(do not use at the end)
Example – 123
Non-Numeric( Alphanumeric) literal
- Maximum 160 characters in length
- Must start and end with quotes
Example – “I AM AN EXAMPLE OF NON-NUMERIC LITERAL” ‘123’
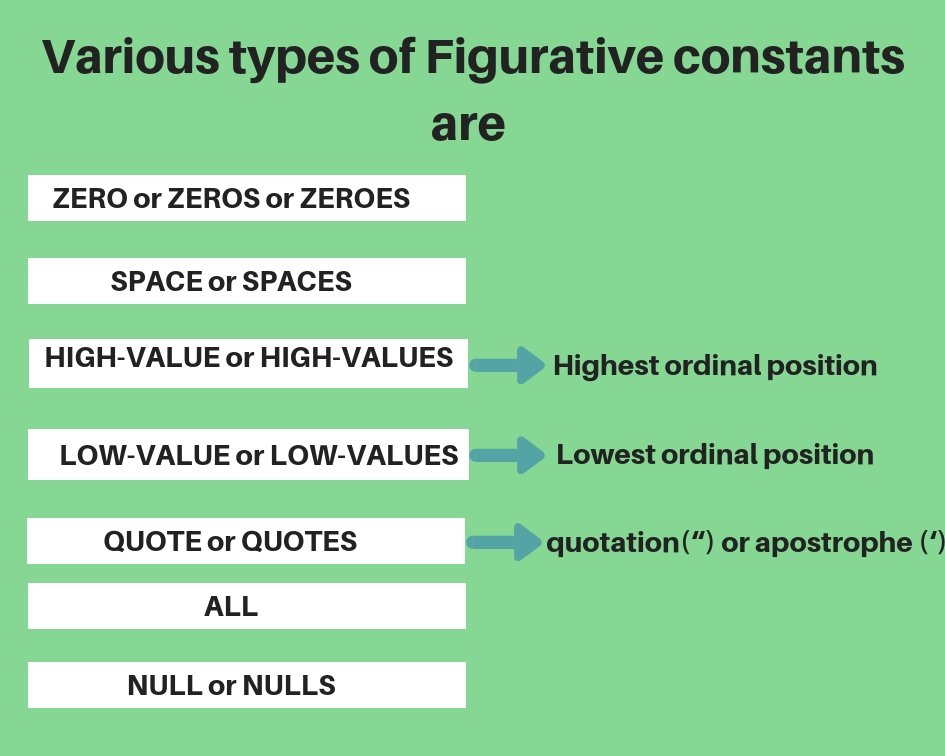
Figurative Constants in COBOL
In COBOL Figurative Constants is reserved words. And these constants are predefined(build in) in COBOL.
CAUTION:
Don’t use HIGH-VALUE/HIGH-VALUES/LOW-VALUE/LOW-VALUES with numeric fields